
The role of HBO in brain resuscitation after CPR
CASE
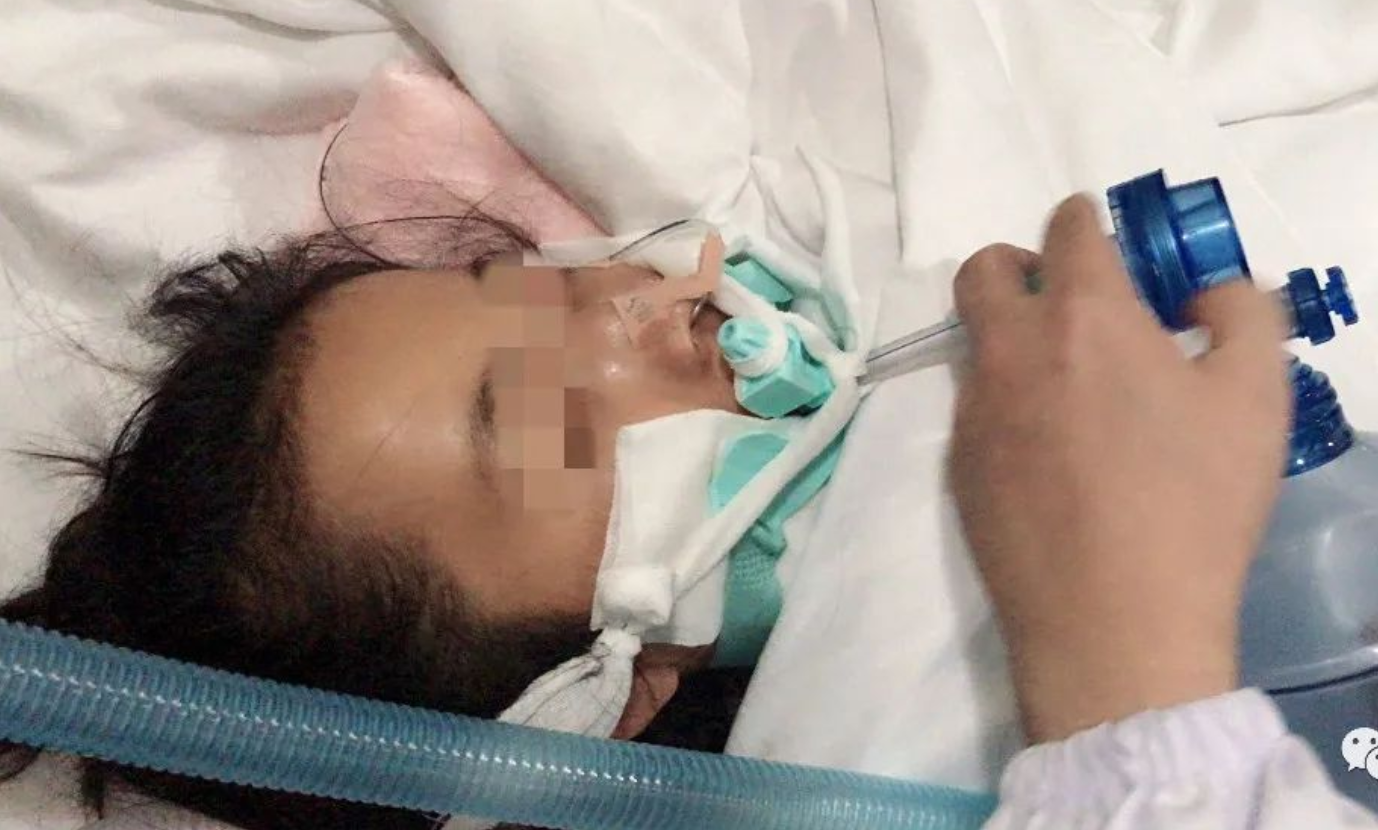
A 13-year-old female patient was admitted to the hospital with "congenital heart disease". After "tricuspid valve replacement + atrial septal repair", ventricular fibrillation, breathing, and cardiac arrest occurred. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation was successful, and the ventilator assisted breathing. The consciousness did not recover, and the muscle strength of the limbs could not be elicited. The next day, accompanied by the ICU doctor, he entered the oxygen chamber for treatment, and was connected to a simple breathing air bag to assist breathing throughout the whole process. After 3 times of 2.5ATA treatment, the child developed involuntary movement of the right upper limb, and his muscle strength was about 2; and he resumed spontaneous breathing. After 5 times, both upper limbs appeared involuntary movements. The treatment pressure was adjusted to 2.0ATA to continue treatment, and consciousness basically recovered after 2 courses of treatment. The child received more than 100 times of hyperbaric oxygen therapy and could walk with assistance. Later, he was transferred to another hospital for further rehabilitation due to mental retardation.
In recent years, with the continuous development and improvement of medicine, after cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) treatment of patients with cardiac and respiratory arrest caused by various reasons, the cardiac and respiratory functions can be recovered, but the cerebral resuscitation is still not ideal. After cardiac arrest, it will cause acute ischemia-hypoxic injury and toxin effects in the brain tissue, resulting in cytotoxic cerebral edema, increased intracranial pressure, aggravated reduction of intracerebral hypoperfusion or cerebral herniation, and increased recurrence of respiration, The risk of circulatory failure, residual neurological dysfunction, or even developing into a vegetative state or death, seriously affecting the quality of life of the patient, the "critical time limit" for the human brain to tolerate circulatory cessation is generally 4 minutes, and the blood flow is completely blocked for more than 4 minutes Brain cells can undergo irreversible changes. Therefore, brain function resuscitation is one of the key links in determining the success or failure of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. A large number of data show that hyperbaric oxygen has irreplaceable effects of drugs and other physical therapy in the process of cerebral resuscitation. It plays an important role in reducing crippling, lethal and vegetative states.

Weifang Huaxin Hyperbaric Oxygen Chamber Manufacture Co.,Ltd
Provide customers with the most timely and thoughtful service!
CONTACT
TEL:+86-536-5070707
FAX:+86-536-5070702
Email:yangjinji@163.com
Navigation
 中文
中文 English
English